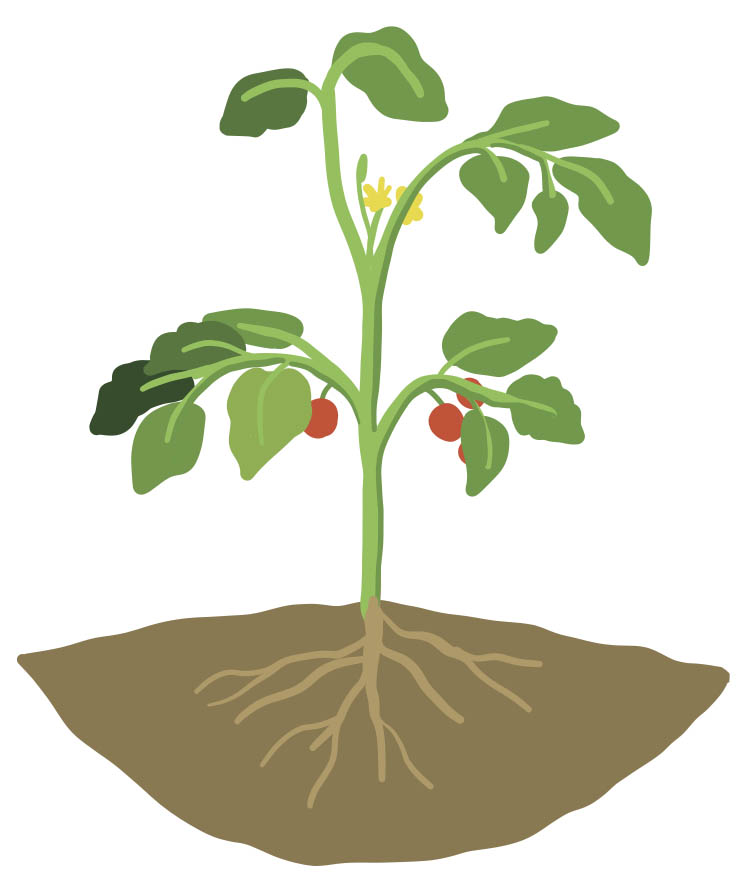
Basic botany of plants
Basic plant botany courtesy of Little Green Thumbs
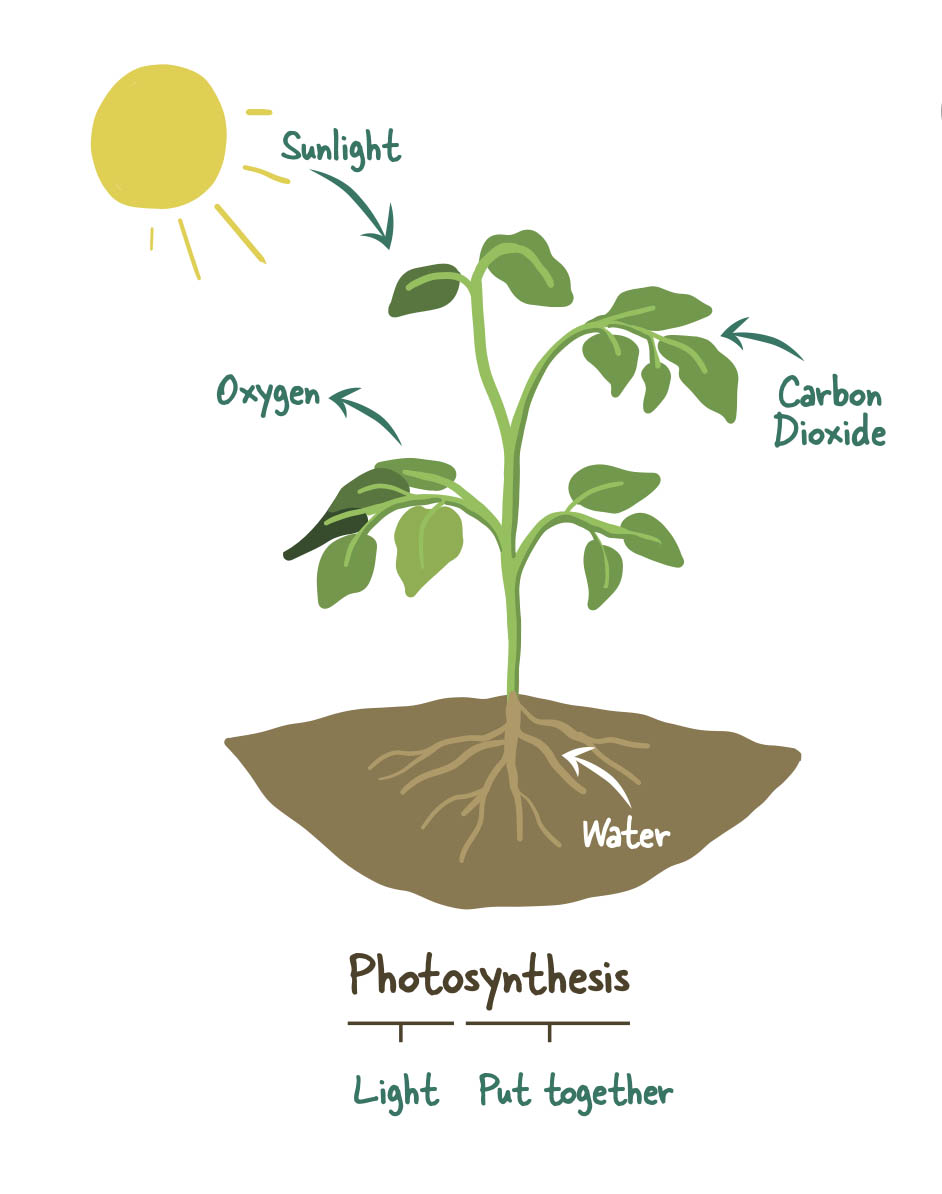
Understanding Photosynthesis
Plants manufacture their own ‘food’ through the process of photosynthesis. A plant will use water, air (carbon dioxide) and light energy to produce glucose, water and oxygen. Photosynthesis takes place primarily in the leaves of a plant. Special leaf structures called chloroplasts, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, account for the plants’ ability to use the suns energy. Plants can use glucose in this form with water for food, and release oxygen back into the air for consumption by animals and humans.
6CO2 + 6H20 + (energy) ––> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide + water + energy from light produces glucose and oxygen.
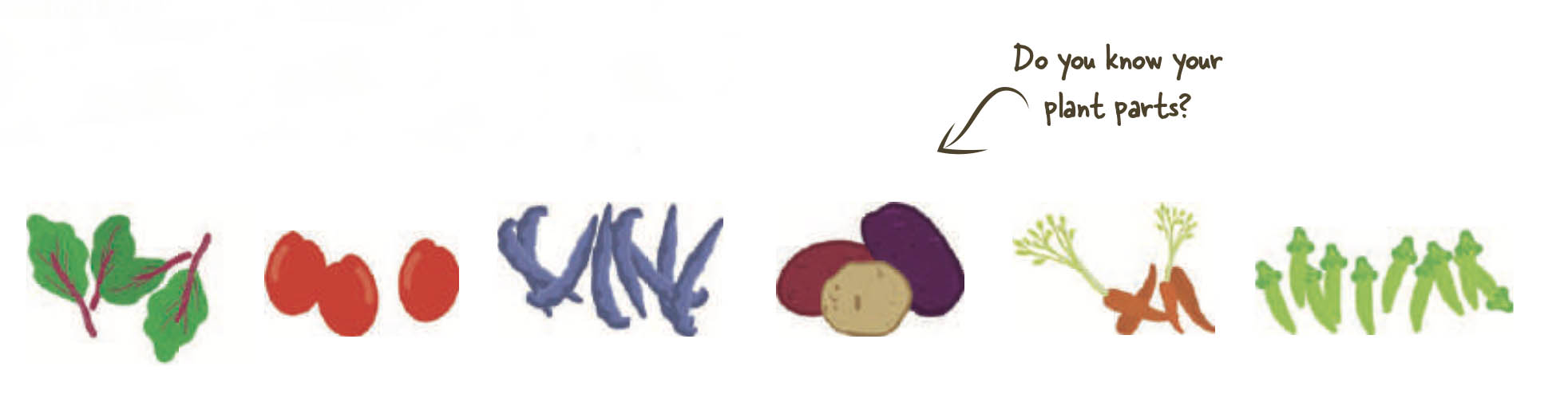
Parts of a plant
Just like most plants share the same basic needs, they also share similar plant parts, which each serve critical functions in the plant.
Leaf
Where photosynthesis and transpiration occur.
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: LETTUCE, KALE, SPINACH, CHARD LEAF
Flower
The site where pollination occurs. Flowers contain the organs for sexual reproduction
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: NASTURTIUM, BROCCOLI, CAULIFLOWER
Fruit
A fruit holds and protects the seeds
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: TOMATO, CUCUMBER, APPLES, ORANGES
Seed
Seeds are formed from the fertilized ovules, after pollination occurs.
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: SUNFLOWER, CORIANDER
Stem
Transports water, food and nutrients to the entire plant.
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: CELERY, KOHLRABI, PEA SHOOTS, POTATO
Root
Absorbs water and nutrients, anchors the plant in place, stores food for the plant
EDIBLE EXAMPLES: CARROTS, RADISHES, BEETS, TURNIPS

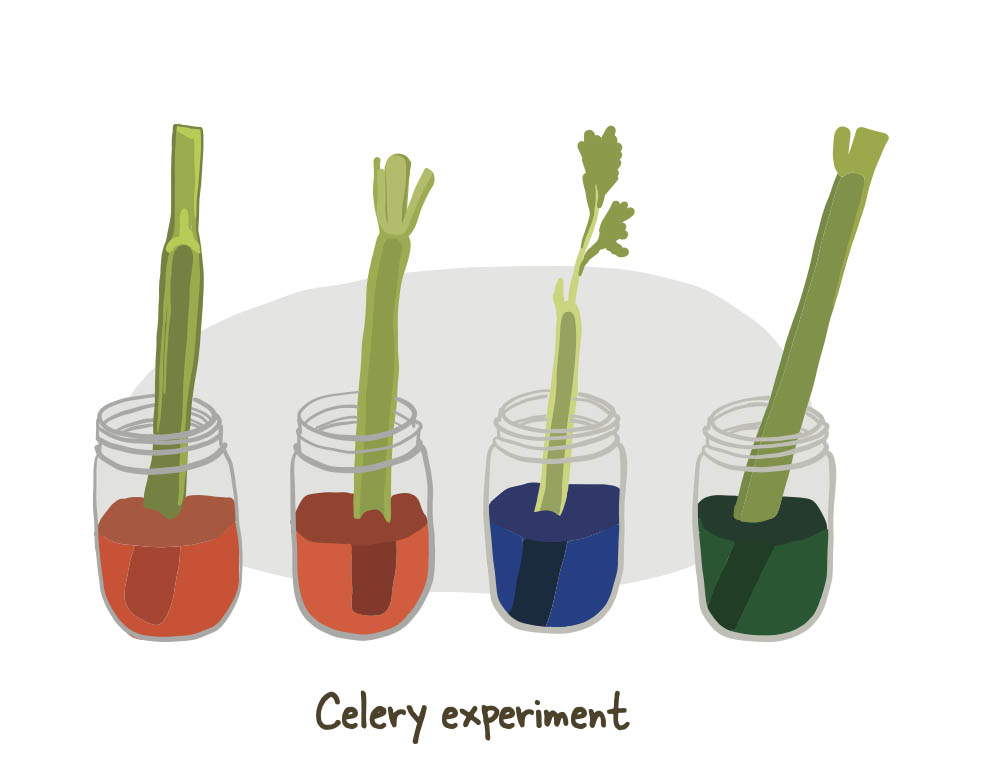
What’s in a Stem?
This is a great experiment to demonstrate how water moves up the stems of plants!
You can use celery, carnations, Napa cabbage, or experiment with different plant. Fill up a couple glass jars with 1 cup of water and add about 10 drops of food colour.
Place your celery stalk, Napa cabbage leaf or flower stem into the water/food colouring mixture.
Leave for one hour or longer for more dramatic effects! You will see that food colouring has travelled up the stems of the plants and coloured the leaves and flowers. You can cut the celery in half to view the Xylem, the tiny tubes that carry water up the stem.
Make your own root viewer!
Observe plant roots by planting into a clear plastic or glass jar. You can fill your jar with soil and plant for seeds around the edges of your jar. Cover the jar with a sleeve of construction paper to block out the light. Every few days remove the sleeve and observe the roots as they grow.

What happens when you block the light from leaves? Observe what happens when part of a leaf is covered up. Try using aluminum foil for this experiment. Cut various shapes and attach shapes to a few large leaves using paper clips. Leave the plant for a few days before removing the coverings. What happened? What is blocked from reaching the leaves and how does this affect the plant? Why is sunlight important to plants. The part of the leaf that was covered will have no starch produced it in because of a lack ofphotosynthesis.
Can you describe your breakfast from a plant's point of view?
You have a bowl of oval, flattened seeds and dried, brown shriveled fruit with fragrant, crushed bark sprinkled on top. You drank a cup of dried, brown shriveled leaves in water with a spoonful of granulated stems and a slice of yellow fruits. What did you eat? (A bowl of oatmeal with raisons and cinnamon, and a cup of tea with a spoonful of sugar and slice of lemon)
Thanks to Little Green Thumbs for providing the information and images on this page.


