Note: Each section on this page contains multiple topics. You will need to click on the tabs in each section for more information.
- Cucumbers are a fairly easy vegetable to grow on the prairies. They are a warm season season plant that need full sun and warm soil of at least 15°C for seed germination and optimal growth.
- They can be direct-seeded in the prairies, but can be grown as transplants in the far north
- Cucumbers do best when they are well watered and fertilized
- Cucumbers benefit from growing in plastic mulches, supported plastic tunnels or crop covers. Crop covers and tunnels must be removed as soon as flowers appear so that bees and other pollinators can pollinate flowers.
- Cucumbers need about 45 - 60 days to maturity, depending on the variety. To extend your harvest, make 2 or 3 successive sowings about 2 weeks apart beginning in late spring when soil is warm.
Cucumbers are classified as cucurbit (Cucurbitaceae) vegetables. The cucurbit family includes cucumbers, summer squash (zucchini), winter squash (hubbard, acorn, spaghetti, butternut, delicata), pumpkins, melons, and gourds.
Since all of these plants share a common ancestor, they all have very similar growing needs and are prone to similar problems.
While they are quite similar, there are some key differences, so to ensure best success so we've broken these into separate articles for easier instruction.
Cucumbers are high in vitamin K, B6, C and riboflavin. Check here for detailed information from the USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference.
The Canadian Food Guide recommends that roughly half of the food on your plate should be fruits and vegetables.
Growing outdoors
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Cucumbers grow best in rich, well-draining, moist soil. You can improve your soil's ability to hold moisture by adding organic matter such as compost or aged, composted manure. Do not use fresh manure as a soil additive. If you think your soil needs remediation, see our Soils and soilless mixes page for detailed advice.
As a vegetable grown for its fruit, they need full sun to produce well and do not tolerate shade.
Cucumbers are best grown outdoors in the ground, be it in raised beds or un-raised/ground level gardens if the soil is suitable. They also grow well in containers, both outdoors and indoors (with supplemental light). They are not typically suitable for straw bale, or other alternative growing methods, but can be grown hyrdoponically.
Cucumbers are a warm season plant that need between 45 and 65 days to maturity. They can be seeded directly into the garden once the soil is warm (at least 18°C). Direct seeding works very well on the prairies, so using seedlings is not necessary.
If you live in the far north, you can grow cucumbers as seedlings. Seedlings can sometimes also be purchased from a local greenhouse.
Starting your own cucumbers plants from seed
- Cucumbers do not like root disturbance from transplanting, so it's important not to start seedlings too early. Seedlings should only be 10-14 days old before planting out (cotyledons have emerged along with only one or two true leaves). Larger transplants will experience transplant shock when they are planted outdoors: plants will not grow for several weeks (or at all) depending on the level of transplant shock they experience. See our video below.
- Start seedlings about 2 -3 weeks prior to transplanting out. You can transplant seedlings as soon as daytime and nighttime temperatures are warm at least 18°C, about 2 weeks after your last average frost free date. For example, in Wollaston Lake (northern Saskatchewan) your plant out date is June 5, so start your seedlings around the first of June for planting out around June 20.
- Jiffy-7's are good for sowing seeds because there is less root disturbance when planting. Soak the Jiffy-7's for 20 minutes in warm water to fully hydrate and expand them. Once they are planted, cover with plastic or a dome and do not water. Remove the plastic once seeds have germinated.
- Another way to reduce root disturbance is to use home-made newspaper pots or peat pots. Fill them with a soil-less mix that contains peat or coir and vermiculite and/or perlite. (Both of these types of pots can be planted directly in the soil, but be sure to bury the rim of these pots. Otherwise the rim acts as a wick and will dry out your seedling.)
- Sow 2 seeds 1 cm deep per JIffy-7 or container and then thin to the strongest plant after they have grown their first set of true leaves.
- Cucumbers prefer warm soil. At 24°C, seeds will germinate in 5 or 6 days. Use a heat mat if you have one, or place pots in a warm spot like the top of the fridge for germination.
- Take care not to over water your seedlings. Soil should be moist like a damp sponge, but not soggy.
- Place seedlings under lights after germination, which is crucial for the growth of healthy seedlings. seedlings require a minimum of 14 hours of light each day.
- Leave a fan blowing on your young seedlings as they grow to help to grow heartier plants and to reduce some seedling diseases. Research has shown that stem diameter can be increased by providing seedlings with constant air movement from an oscillating fan – or by lightly brushing seedling tops with a tea towel or stick at least 20 times daily.
- For more details, check out our article on growing your own seedlings.
The ideal cucumber transplant:
- has no more than two sets of true leaves. The first leaves that grow are not true leaves. They are "seed leaves" called cotyledons and are round. All leaves that grow after these are true leaves.
- is dark green in color.
- has a good root system but is not root-bound (tight, hard ball of roots) or has lots of roots growing out of the Jiffy-7.
- has a stem that is strong and sturdy. The internodes (spaces between leaves along the stem) will be small. seedlings that are too tall will tend to break and dry out more easily once planted out into the garden.
- Fertilizing recently planted seeds or young emerging seedlings is not recommended. Start fertilizing a few days after they have been planted out in the garden using 20-20-20 water-soluble fertilizer once or twice a week. Mix according to label directions.
Harden off seedlings prior to planting out by moving them outdoors into a sheltered, frost-free location at least 3 days prior to transplanting.
Don't forget to label what you planted. It's also helpful to draw a map to help you track planting locations and success each year. This information is critical if you're rotating your crops to help prevent insect and disease issues.
Timing
- Cucumbers may be direct seeded in the garden on the prairies or planted as seedlings in the far north. See our transplants tab for tips on growing or purchasing your own transplants.
- You can transplant seedlings as soon as daytime temperatures are above 18°C. For example, in Wollaston Lake (northern Saskatchewan) your plant out date is June 5, so start your seedlings around the first of June for planting out around June 20.
- Transplants must be hardened off before transplanting outdoors. Cucumbers do not tolerate cool soil or air temperatures.
- Sow 3-4 seeds 2 cm (1″) deep and 25 cm apart within the row. Thin to the strongest seedling.
- Sow 2 or 3 successive plantings starting after the soil is warm.
Planting instructions for seedlings
- When planting, cover the entire transplant “plug” or seed ball with soil to prevent the plant from drying out. If using newspaper pots or peat pots, make sure they are quite moist before planting and remove the rims of the pots. Exposed rims, peat or coir within the plug will act as a wick, drawing water away from the transplant and drying out the root ball.
- Try not to disturb the roots when planting.
- Seedlings should be spaced 25 cm apart within the row, allowing 90 cm between rows.
- Water the transplants in with 10-52-10 soluble fertilizer, mixed according to the directions on the label. This is only done once, to encourage good root development. See the "Care Once Planted" tab for how to fertilize for the rest of the growing season.
Cutworm prevention
If you have had cutworm problems in your garden, place a collar around your seedlings right after planting. Make collars out of toilet paper rolls, or any tin can or plastic container such as a yogurt container with both ends removed. Insert the collar at least 5 cm in the ground to prevent cutworms from feeding on the stems of your seedlings.
Although any cucumber can be pickled, the "pickling" types tend to be shorter and more suited to pickling. Smaller cucumbers also have the advantage of having fewer seeds. Some of the pickling types can grow to be long and large, so it's best to harvest them before they reach their full size.
Slicing cucumbers are good for fresh eating.
Cocktail or snacking cucumbers are cucumbers that have a soft skin and are mature when they are only 15cm long (these are the type sold in packages of 5 or 6 in the grocery store).
A third type of cucumber are called "greenhouse" or English or parthenocarpic cucumbers. They are hybrids that have been bred for all female flowers. They do not need pollination and produce seedless fruit. However, if these are planted near other types of cucumbers and pollinating insects are present, cross pollination is still possible and they may produce cucumbers with seeds. Greenhouse cucumbers are meant to be grown in the greenhouse and do not yield well when grown outdoors.
Here are cultivar recommendations from the North Dakota State University Cultivar Trials, as they share a similar prairie climate and soils. You may download their list here:North Dakota State University Vegetable Cultivar Recommendations for 2021
- Pickling: Alibi, Calypso, Eureka, Homemade Pickles, H-19 Little Leaf
- Slicing: Dasher II, Diva, Fanfare, General Lee, Mercury, Muncher, Orient Express II, Raceway, Raider, Salad Bush, Silver Slicer, Straight Eight, Summer Dance, Sweet Slice, Sweet Success, Tasty Green
The following cultivars are recommendations from the University of Saskatchewan vegetable program field trials which were conducted from 1989 through 2016. Although this information is no longer current, some may find it useful.
- Pickling: Atomic, Ballerina, Cool Breeze, Cool Breeze Improved, Cross Country, Eclipse, Eureka, Europick, Fancipak, Gherkin, KFR, Northern Dawn, Zapata
- Slicing: Babylon, Darlington, Dasher II, Diomede, Emperator, Fanfare, General Lee, Indio, Indy, Jazzer, Marketmore, Natsuhikari, Olympian, Raider, Speedway, Straight 9, Ultra Pak
Cucumbers should have about 2.5cm of water per week early in the season. By mid-July, provide 2.5cm of water, twice weekly.
Dry soil may result in smaller cucumbers and cause them to become bitter.
Apply soluble 20-20-20 fertilizer every week prior to fruit set. Increase fertilizing to twice a week after fruit set.
Pick weeds as they appear.
To conserve soil moisture and reduce weeding, apply a thick layer of mulch around your plants, whether in the garden or in a container. Ensure the mulch is not resting against the stems of the plants.
Install a trellis or other support to grow cucumbers vertically. This saves space and improves air circulation which can prevent or reduce problems such as powdery mildew.
Cucumbers benefit from growing in plastic mulches, supported plastic tunnels or crop covers. Crop covers and tunnels must be removed as soon as flowers appear so that bees and other pollinators can pollinate flowers.
Cucurbits have both male and female flowers on their vines. Male flowers are the first flowers to appear on the plant. It is normal for some of these initial male flowers to fall off – don’t be alarmed. Female flowers appear 7-10 days after the male flowers start to appear. The female flowers are identified by what looks like a small fruit where the stem meets the flower. This ‘small fruit’ is missing on the male flowers.
Cucumbers are not suited to fall seeding.
Cucumbers are best grown as transplants in the far north. Direct seed only if the soil is very warm. To pre-warm soil, cover soil with a layer of clear plastic 2 weeks before planting. Secure the edges to keep the plastic from blowing away. Remove the plastic after planting.
Cucumbers do well in containers. Black or dark coloured containers help keep the soil and root system warm.
Cucumbers benefit from black plastic mulch, row covers and clear low plastic tunnels to keep the environment around the plants warm.
Loading...
See our preservation section for more videos.
Growing in containers
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Cucumbers are excellent for container growing, whether indoors or out. Supplemental lighting is needed if growing indoors.
Select a container that is at least 8 litres (2 gallons) and has drainage holes in the bottom. Dark containers help to keep the root system warm.
Plant 2 - 3 cucumber seeds into the container and then thin to the strongest seedling after they get their true leaves.
Place a layer of mulch on top of the soil in the container to keep soil moisture even.
Provide a trellis or stakes to grow vertically.
See: Vegetable container gardening
Any cucumber will work in a container. Patio cultivars are very dwarf vines but produce fewer cucumbers than the longer vines.
Saving seeds
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Seeds are expected to be shelf-stable for one year from date of sale if purchased from a reputable retailer. If you wish to save your seeds beyond that, you should store them in the fridge in a jar. Seeds lose viability quickly if they dry out too much or get too warm.
The life expectancy of cucumber seed stored under favourable conditions is about five years.
Seeds stored under less favourable conditions will show poor germination after just a single year of storage. Beyond this, you can expect your germination rates to go down (ie. not all of your seeds will grow, but some might). To test your seeds, you can do a simple germination test. Follow the link for instructions. If you are still getting some seeds germinating, seed more thickly and thin any extra.
Cucumber seeds can be saved from “heritage” or “open-pollinated” plants. If the plant tag or seed package from the original plant says “hybrid”, the plants grown from seeds collected from hybrid plants won't look the same next year.
This fermentation method gets rid of the pulp on seeds.
- Let two or three cucumbers ripen as long as possible on the plant before frost. Over-ripe cucumbers that are beginning to turn yellow are good for seed saving. Avoid saving seeds from diseased plants as disease can be carried over on seeds.
- Slice the cucumbers in half lengthwise and scoop the seeds into a bowl.
- Seeds have a slimy coating called pulp. Put the seeds and pulp in a container with a lid. Label the container with cucumber name and year. Add some water – the seeds and pulp will float to the top.
- Keep this in a warm place for 3 – 5 days. The warmth causes the pulp to rot and ferment. This releases the seeds which will drop to the bottom of the container.
- Once the seeds have separated from the pulp and dropped to the bottom of the container, add some water and pour off the pulp.
- Fill the container again. Let the seeds sink to the bottom and pour off the water.
- Now dump the seeds and water into a fine mesh strainer. Rinse under cool water.
- Put the seeds on a coffee filter or a plate and spread them out to let them dry. It may up to a week for the seeds to dry completely. Seeds are dry when they can be snapped in half.
Another way is to save seeds is to simply wash the seeds to remove as much pulp as possible. Strain the seeds in a colander and spread them on a plate or tray to dry. Before you plant these seeds, pre-soak them in water for a few hours to get rid of the coating.
How to store seeds
Vegetable seeds can keep for several years if you store them properly. Seeds should be stored in a cool, dry, dark place. Moisture, heat and light can cause seeds to sprout or rot.
- Place your seeds in envelopes or make your own envelopes out of foil or waxed paper. Label with name of the seeds and the date (month and year) you harvested them.
- Place your envelopes inside an airtight container. To help keep seeds dry, place about a tablespoon of dry powdered milk in a paper towel or piece of cloth, secured with a twist tie or piece of string. The powdered milk will absorb humidity and keep seeds dry inside the airtight container.
- Put the container in the refrigerator. Do not store seeds in an unheated shed or garage. These places are either too moist and/or too cold for seed storage.
Harvest
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Check your seed package for days to maturity. Cucumbers can be harvested as early as mid-July on the prairies up until fall frost. As cucumbers start to mature, they may need to be harvested daily.
Harvest cucumbers in the morning (this is when they have the highest amount of water in them – they will be crunchy), cool cucumbers immediately after picking and store them at 5-10°C; will store 2 + weeks.
It is better to harvest immature than over-mature cucumbers for taste and quality. Over-mature cucumbers are prone to becoming bitter with thicker skin. Once cucumbers are starting to turn yellow, they are over-ripe and will not taste good.
Immature cucumbers tend to have a shorter storage life (moisture loss). Field slicers have thicker skin and have a longer storage life than greenhouse types with very thin skin.
Pick cucumbers daily and select the size that works for your needs. Under-mature cucumbers that are 5 - 8 cm long are good for pickles, 10 - 15 cm long for dills and larger ones can be sliced for bread and butter pickles.
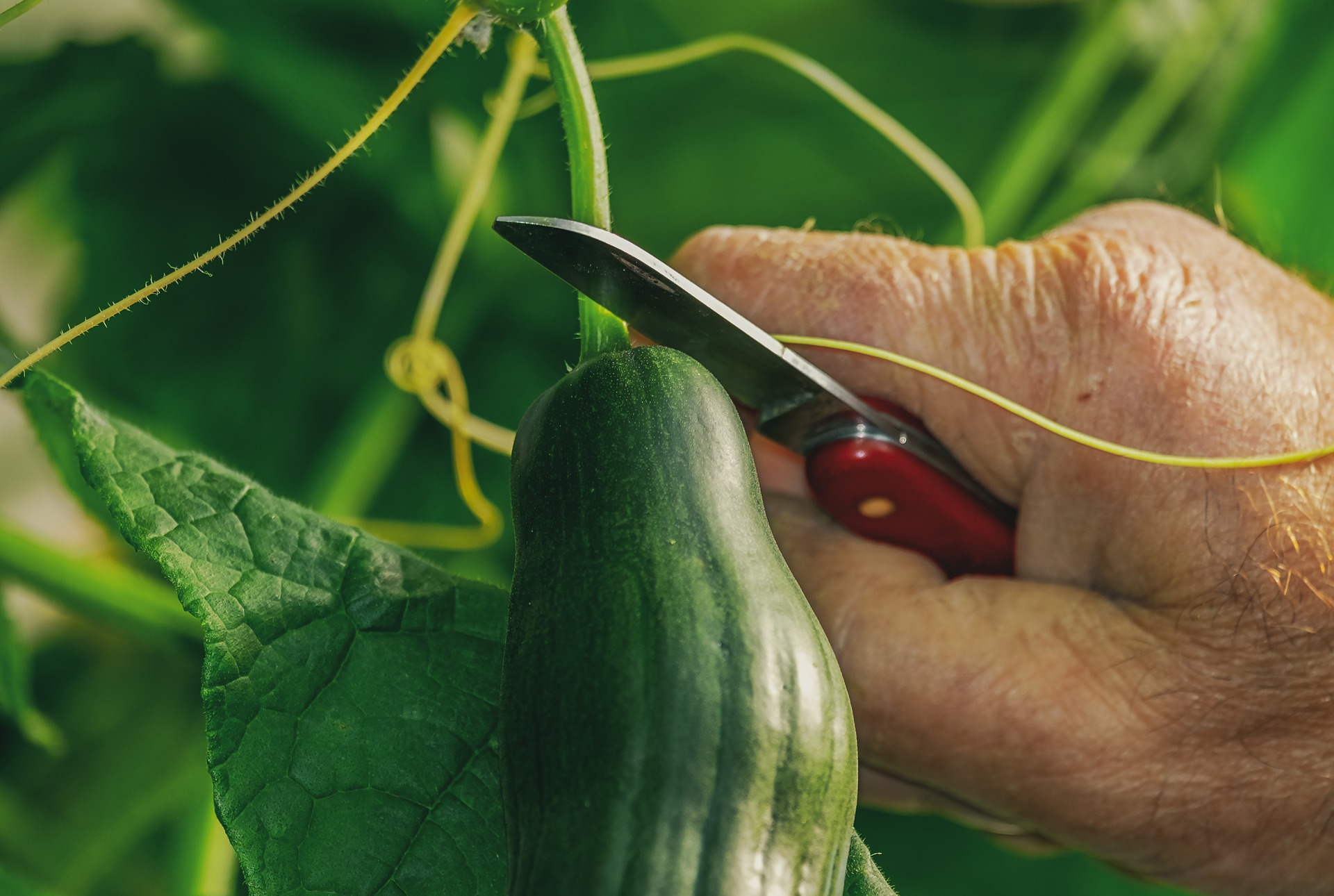

Ripe cucumbers tend to come off the plant easily with a gentle tug. Otherwise, use a sharp knife or scissors to cut the cucumber from the stem. Leave about 1 cm of stem. Do not cut into the cucumber itself.
Cucumbers have a high respiration rate, especially the thin-skinned varieties. It is important to keep them cool during harvest.
Storage
Cucumbers should be used soon after harvest. They can be stored temporarily in the crisper in the fridge for 1 - 3 days but are prone to chilling injury if stored cold for longer periods of time. Otherwise, they can be stored at 5-10°C (a cool room) and will store about 2 weeks.
If you're hoping to store them longer than a month, you will need to use other preservation methods such as freezing, fermenting, canning or drying.
For detailed advice on other potential spaces or methods, see our cold storage page.
Cooking and preserving
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Cucumbers can be canned (pickled), fermented, dehydrated (dried) or frozen.
Coming soon
Loading...
Troubleshooting
Click on the tabs above for more information!
Cucumbers are relatively low maintenance. Providing their water, light and soil needs are managed they don't tend to get a lot of issues.
Cucumbers need a good supply of water and fertilizer to do well.
Ensuring that you maintain healthy soil with adequate organic matter and use row covers to prevent insect problems will go a long way towards preventing most issues.
See the Common problems tab on this page for advice on other specific cucumber issues.
Common problems include powdery mildew and pollination problems.
Loading...
Common questions
Cucumber plants contain a natural compound called cucurbitacin, which is normally found in the roots, stems and leaves of the plant. However, this compound tends to spread into the cucumbers when the plant is under stress from hot temperatures and/or lack of water.
The bitter compounds tend concentrate in the stem end and just under the skin of the cucumber. Cut off the stem end and peel the skin to avoid the bitterness. Ensure that your plants are well-watered, especially in hot weather.
Poor fruit set on female flowers can happen when there is a lack of female flowers on the plant and/or poor pollination by bees or insects.
All cucurbits have both male and female flowers on their vines. Male flowers are the first flowers to appear on the plant. It is normal for some of these initial male flowers to fall off – don’t be alarmed. Female flowers appear 7-10 days after the male flowers start to appear. The female flowers are identified by what looks like a small fruit where the stem meets the flower. This ‘small fruit’ is missing on the male flowers.
Poor pollination can also be due to a lack of pollinators. Cold, rainy or cloudy weather discourages bees and other insects from flying around to pollinate. Insecticide use in the garden kills pollinators and can be another cause.
If you are using row cover, remove the covers when the plants are flowering to allow pollinating insects to access the plants. Similarly, if you are growing in a greenhouse, open doors and vents to allow pollinators to enter.
You can help pollinate your plants. Using a small brush or q-tip, dab the center of a male flower – these are the flowers with a large anther in the middle which contains the pollen. The pollen will stick to the paintbrush as it would on a bee. Transfer the pollen to the centre of the female flowers. Female flowers lack an anther and have what looks like a small swelling just beneath the flower. Or, you can simply pick a male flower and gently touch the anther to each of the female flowers. Repeat for all of the flowers. It’s best to do this early in the morning as cucurbit flowers open early and only last for one day.

Research and student activities
An interesting archeological paper about early cucurbit use by Indigenous peoples:
More research:
Organic cucurbit production - Dalhousie University
Managing cucurbit disease - Michigan State University


